| Length: 23 inches | Wingspan: 55 inches | Seasonality: Non-resident in South Dakota |
| ID Keys: Large size, mottled brown overall (darker on wings), large powerful bill, black legs | ||
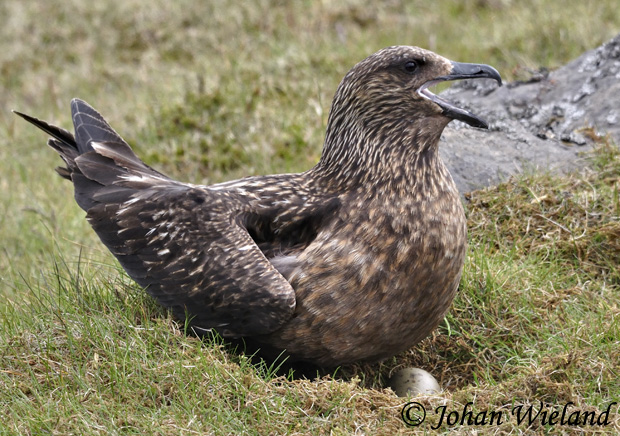 The
Great Skua is a large, dominant species of the North Atlantic. They
breed in Iceland and near Great Britain, but disperse widely in the Atlantic
after breeding, including off the Atlantic coast of North America.
Aggressive feeders, they often feed on fish, but will take both young and
adult birds, and often forage by harassing other birds to drop their catch.
They are equally as bold around their nesting sites, aggressively defending
their territory from all intruders, including humans that stray too close.
The
Great Skua is a large, dominant species of the North Atlantic. They
breed in Iceland and near Great Britain, but disperse widely in the Atlantic
after breeding, including off the Atlantic coast of North America.
Aggressive feeders, they often feed on fish, but will take both young and
adult birds, and often forage by harassing other birds to drop their catch.
They are equally as bold around their nesting sites, aggressively defending
their territory from all intruders, including humans that stray too close.
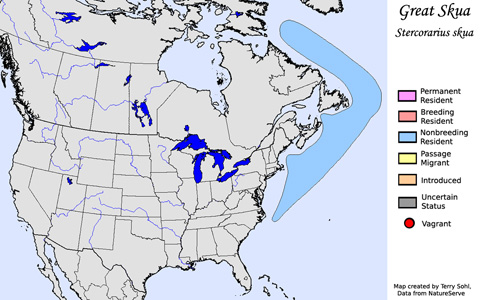
Habitat: During the summer breeding season, Great Skuas are found on open, treeless islands in the northeastern Atlantic. They are usually far from shore at other seasons.
Diet: Primarily feeds on fish when out on the open ocean, such as during the non-breeding season. They will also feed heavily on the eggs and young of other seabirds if the opportunity is present, and will even take adult birds. Opportunistic, they will also sometimes feed on carrion, insects, mice and other rodents, and other small animal life.
Behavior: Foraging techniques depend upon location and season. When on the open sea, they usually feed by dipping down to the surface of the water from flight, or by swimming on the water's surface and grabbing prey with their bill. They will often harass other birds, forcing them to give up their fish or other prey.
Nesting: The Great Skua's nest is a shallow scrape on the ground, with a sparse lining of vegetative material. The female usually lays 2 eggs, and both parents help to incubate them. When the eggs hatch, the female usually stays with the young while the male feeds the young through regurgitation. The young fledge after about 6 or 7 weeks.
Song: In North America, away from their breeding grounds, they are normally silent.
Migration: Breeds on islands in the northeastern Atlantic, primarily Iceland and islands north of Great Britain. Non-breeding birds disperse across the Atlantic, including off the coast of North America, but also as far south as the Atlantic coasts of South America and Africa.
Interactive eBird map: Click here to access an interactive eBird map of Great Skua sightings
Similar Species: South Polar Skua
Conservation Status: Global populations are not very large, but they are stable and there are currently no major threats. The IUCN lists the Great Skua as a species of "Least Concern".
Further Information: 1) Royal Society for the Protection of Birds - Great Skua
2) BirdLife International - Great Skua
3) Joint Nature Conservation Committee - Great Skua
Photo Information: Photo taken by Johan Wieland - Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution NoDerivs 2.0 Generic License.
| Click below for a higher-resolution map |
 |
| South Dakota Status: Non-resident in South Dakota |
Additional Great Skua Photos (coming soon!!)
