| Length: 4.5 inches | Wingspan: 6 inches | Seasonality: Non-resident in South Dakota |
| ID Keys: Rich brown upperparts, light underparts with "scaling" on flanks and breast, dark bill | ||
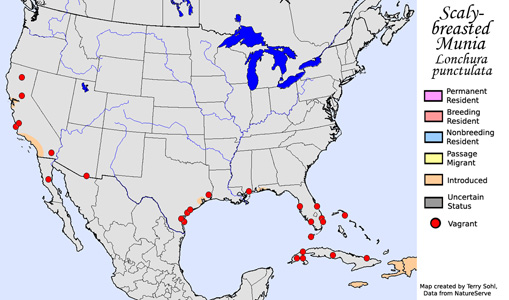
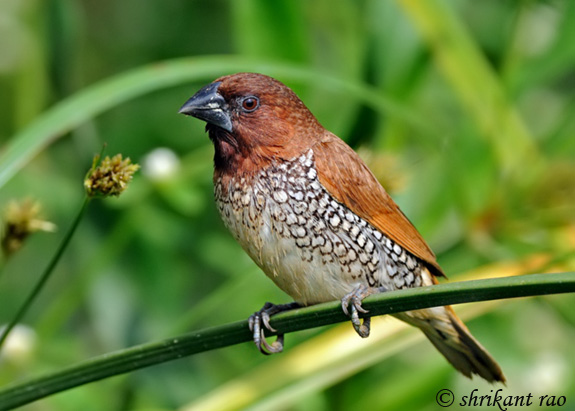 The
Scaly-breasted Munia is native to India, southern China, and much of
southeastern Asia. They are a popular cage bird in many parts of the
world, where they are often called "Nutmeg Mannikin" or "Spice Finch".
Given their widespread popularity, escapees have established populations in
many parts of the world. In the United States, the American Birding
Association recognized them as a permanent species in 2013 based on large
breeding populations that have become established in southern California.
Breeding populations also occur in and around the San Francisco Bay in
California, near Houston, Texas, and locally elsewhere in the southern
United States. They are also well established on several islands in
the Caribbean.
The
Scaly-breasted Munia is native to India, southern China, and much of
southeastern Asia. They are a popular cage bird in many parts of the
world, where they are often called "Nutmeg Mannikin" or "Spice Finch".
Given their widespread popularity, escapees have established populations in
many parts of the world. In the United States, the American Birding
Association recognized them as a permanent species in 2013 based on large
breeding populations that have become established in southern California.
Breeding populations also occur in and around the San Francisco Bay in
California, near Houston, Texas, and locally elsewhere in the southern
United States. They are also well established on several islands in
the Caribbean.
Habitat: Found in grassland habitats in their native range, particularly in areas near sources of fresh water. They will feed heavily on grain if available, and can also thus be found around grain fields and rice paddies. Introduced populations in the United States are found in a variety of open habitats with suitable foraging opportunities, including farmland, urban edges, and grassy and shrubby fields.
Diet: Feeds heaviliy on seeds, but will also sometimes feed on berries and small fruits. They will feed heavily on grain and rice if available. On occasion they will also feed on insects, and have been noted to often feed on algae prior to the breeding season.
Behavior: Scaly-breasted Munia are a very social species, often found foraging in large flocks.
Nesting: The nest of a Scaly-breasted Munia is a large dome, made of grasses, leaves, or other vegetative material, with a side entrance. It is typically placed in a tree or shrub, but they will also utilize man-made structures and place nests in protected locations such as window ledges or under eaves of buildings. The female lays 4 to 8 eggs, and both parents help to incubate them. The young hatch after about 2 weeks. Both parents feed the young, which fledge about 3 weeks after hatching.
Song: Has a variety of vocalizations, particularly when communicating in flocks. Typical calls include a sharp chip note used in alarm, short whistles, and a chit-tee chit-tee chattering. During courting, males will sing a very quiet, variable, long song of a series of whistled and chattered notes and phrases.
Migration: Considered a non-migratory resident throughout its range.
Interactive eBird map: Click here to access an interactive eBird map of Scaly-breasted Munia sightings
Similar Species: Distinctive if seen well.
Conservation Status: The Scaly-breasted Munia is common in many parts of their broad range (both in their native range, and in the many areas where escaped birds have established populations). The IUCN lists the Scaly-breasted Munia as a species of "least concern".
Further Information: 1) BirdLife International - Scaly-breasted Munia
2) Whatbird - Scaly-breasted Munia
3) Birds in Backyards - Nutmeg Mannikin
Photo Information: Photo by Shrikant Rao - Photo licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic License
Additional Photos: Additional Photos Coming Soon!!
| Click below for a higher-resolution map |
 |
| South Dakota Status: Non-resident in South Dakota |
Additional Scaly-breasted Munia Photos (coming soon!!)
