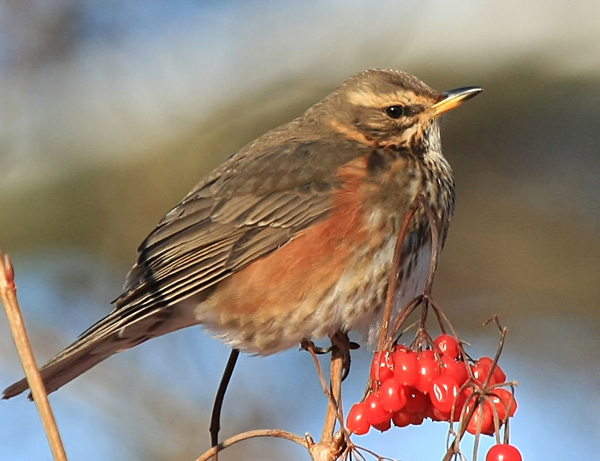
| Length: 8.25 inches | Wingspan: 13.75 inches | Seasonality: Non-resident in South Dakota |
| ID Keys: Dark brownish-gray upperparts, white underparts with dark spots on breast , orangish-red flanks, obvious white supercillium, yellow bill with black tip | ||
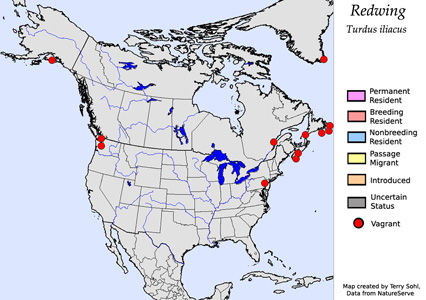
 The
Redwing is a Eurasian thrush species, with a breeding range that extends
from Iceland in the west, eastward through northern Great Britain,
Scandanavia, and throughout much of Russia. In North America they are rare
vagrants, with the majority of sightings occurring in the northeastern U.S.
and southeastern Canada. Breeding populations have been expanding in
some areas, and they now can also be found as semi-regular breeding birds in
southern Greenland. The species has been in a strong decline in the European
part of its range in recent decades, with potential causes including habitat
loss, direct trapping and killing of some birds in the Mediterranean region,
and possibly the effects of climate change.
The
Redwing is a Eurasian thrush species, with a breeding range that extends
from Iceland in the west, eastward through northern Great Britain,
Scandanavia, and throughout much of Russia. In North America they are rare
vagrants, with the majority of sightings occurring in the northeastern U.S.
and southeastern Canada. Breeding populations have been expanding in
some areas, and they now can also be found as semi-regular breeding birds in
southern Greenland. The species has been in a strong decline in the European
part of its range in recent decades, with potential causes including habitat
loss, direct trapping and killing of some birds in the Mediterranean region,
and possibly the effects of climate change.
Habitat: Found in a variety of habitats. They are often found in and around forest clearings and forest edges, and will also colonize second-growth forest. Riparian areas, open woodlands, and scattered groves of trees may also hold Redwing. They have also become accustomed to a human-influenced landscape, and can be found around shrubby hedgerows, parks, suburban gardens, and other anthropogenic landscapes.
Diet: Feeds on insects, spiders, earthworms, snails, and other small invertebrates. They also feed heavily on fruits and berries, particularly during migration and in the winter months.
Behavior: Foraging is often done on the ground, but they may also glean insects from vegetation or forage for fruits in berries in bushes and trees.
Nesting: The nest is a cup built of grasses, mosses, and twigs, bound together with mud and lined with fine grasses and leaves. The nest is sometimes placed on the ground, but may also be placed low in a bush or tree, near a fallen log or tree stump, or sometimes on a human structure. The female lays between 3 and 6 eggs, and she alone incubates them. The eggs hatch after about 13 days, and both parents help to feed and raise the young. The young leave the nest about 2 weeks after hatching.
Song: The song is a descending series of 4 to 6 musical notes, typically followed by a quieter series of warbled notes at the end.
Migration: Migratory. During the summer breeding season, they may be found in Iceland, far northern Great Britain, Scandanavia, and eastward throughout much of Russia. In winter, they move south and west, with much of western Europe and the Mediterranean region (including North Africa) holding overwinter birds. Some may also overwinter in the Middle East and southwest Asia.
Interactive eBird map: Click here to access an interactive eBird map of Redwing sightings
Feeders: Redwings have occasionally attended feeders for offered fruits, berries, and nut meal.
Similar Species: At first glance any vagrant Redwing found in the United States is most likely to be confused with American Robin. Plumage difference are obvious, however, including the spotted white underparts of the Redwing compared to the solid orange-red underparts of a Robin. They also could potentially be confused with another very rare North American vagrant, the Eyebrowed Thrush.
Conservation Status: Populations have been in strong decline in the European portion of their range. Asia populations are less well understood, but they are thought to also be in decline in that part of their range. As a result, the IUCN lists the Redwing as a "Near Threatened" species.
Further Information: 1) BirdLife International - Redwing
2) WhatBird - Redwing
3) Royal Society for the Protection of Birds - Redwing
Photo Information: Photo by Dornenwolf - Photo licensed under Creative Commons Attribution ShareAlike 2.0 Generic License
| Click below for a higher-resolution map |
 |
| South Dakota Status: Non-resident in South Dakota |
Additional Redwing Photos (coming soon!!)
