| Length: 6.5 inches | Wingspan: 10 inches | Seasonality: Non-resident in South Dakota |
| ID Keys: Breeding male has chestnut throat and face, white crown stripes and cheeks. | ||
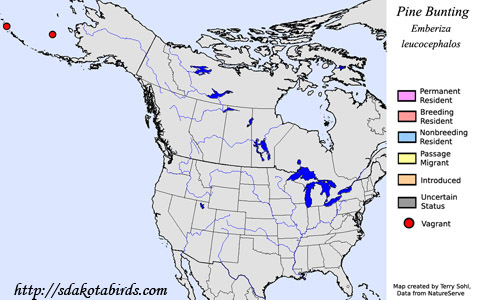
 The
Pine Bunting is an Asian species. They normally breed in eastern
Russia, and locally in northern Mongolia, northern China, and eastern
Kazakhstan, with northern populations moving southward to central China and
from northern India through southern Kazakhstan. In North America,
they are only rare vagrants, being found on a handful of occasions in the
Aleutian Islands or St. Paul Island of Alaska.
The
Pine Bunting is an Asian species. They normally breed in eastern
Russia, and locally in northern Mongolia, northern China, and eastern
Kazakhstan, with northern populations moving southward to central China and
from northern India through southern Kazakhstan. In North America,
they are only rare vagrants, being found on a handful of occasions in the
Aleutian Islands or St. Paul Island of Alaska.
Habitat: In its breeding range, it is found in open boreal forest, preferring evergreen forest and avoiding pure deciduous areas. They can also be found in grasslands steppes with scattered trees and shrubs. Outside of the breeding season they will utilize a broader array of habitats, including open forest, forest clearings and edges, agricultural land, roadsides, parks and suburban areas, and shrubby grasslands.
Diet: Feeds heavily on seeds in all seasons, but during the breeding season will also feed heavily on insects. They have learned to take advantage of agricultural areas, gathering in flocks during the non-breeding season to feed on waste grain in agricultural fields.
Behavior: Tends to forage on the ground or very low in vegetation, even when on their forested breeding grounds. Gregarious outside of the breeding season, often forming large flocks that feed in agricultural fields and other areas with concentrations of seeds and other food items.
Nesting: The nest is constructed in a protected shallow depression on the ground, such as at the base of a rock, under a shrub or other standing vegetation, or next to a fallen log. The nest is constructed of twigs, grasses, and roots, lined with finer material such as fine rootlets and grasses and/or animal hair. The female lays between 3 and 6 eggs, and the young hatch after about 13 days.
Song: Click here to visit a site for listening to a Pine Bunting song.
Migration: Migratory, moving to central and southern Asia in winter, although there is overlap between breeding and non-breeding zones.
Interactive eBird map: Click here to access an interactive eBird map of Pine Bunting sightings
Similar Species: Often compared to Yellowhammer, a species not found in North America. They have hybridized with Yellowhammer before.
Conservation Status: Populations are found across a very wide geographic area, they are common in many areas, and populations appear to be stable. The IUCN lists the Pine Bunting as a species of "Least Concern".
Further Information: 1) BirdLife International - Pine Bunting
2) AviBirds.com - Pine Bunting
3) BirdFellow - Pine Bunting
Photo Information: Photo by Sergey Yellseev. Photo licensed under Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial NoDerivs 2.0 Generic License
| Click below for a higher-resolution map |
 |
| South Dakota Status: Non-resident in South Dakota |
Additional Pine Bunting Photos (coming soon!!)
